In gambling, the odds describes the ratio of the size of the potential winnings to the gambling stake;"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (

Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds versus risk ratio
Odds versus risk ratio- Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notFor instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an odds ratioA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical
If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not toOdds Ratio Definition odds ratio – a measure of effect size, describing the strength of association or nonindependence between two binary data values In a case control study, this is the ratio between the fraction with the risk variant versus nonrisk variant in the groups of affected versus the controls, ie expressed in terms ofRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratio
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratioThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population, Relative risks versus odds ratios Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus for the prevention of any diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use in hospital A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial study design was used




Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram
Relative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test Now we can't calculate the Relative Risk of dying from lung cancer if you're a smoker vs a nonsmoker But the Odds ratio still works, and we can easily calculate it 9,333 x 5,003 = 14 (I used the same proportions as above, just made the 4,997 x 667 samples bigger)The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Odds ratio is a very effective way of determining association between two variables, mostly influence of one factor on the outcome of interest If strong enough, and the statistical analysis robust enough, it can even determine causality ie prove a cause – effect relationship between a risk factor and disease or an adverse effect and
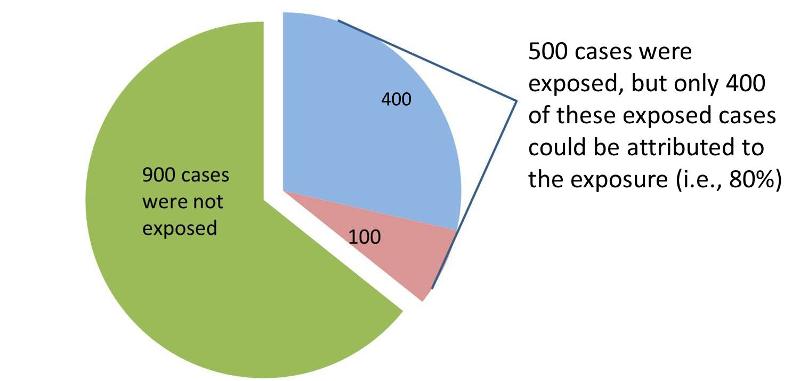



Measures Of Association




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
An Odds Ratio (OR) then is simply the comparison of two odds, OR=Odds (A)/Odds (B) The Relative Risk (RR) is simply the comparison of two risks or probabilities, RR=Probability (A)/Probability (B) This is made more clear when the term is referred to as the Risk Ratio Let's look at this graphically Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios 2, while a 12Odds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used
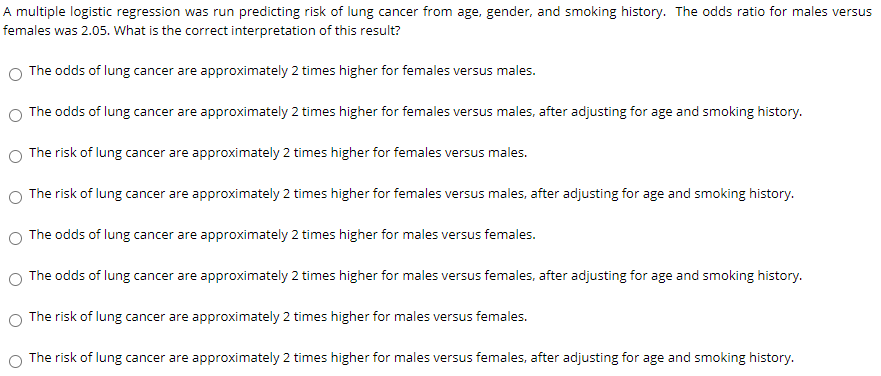



A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com
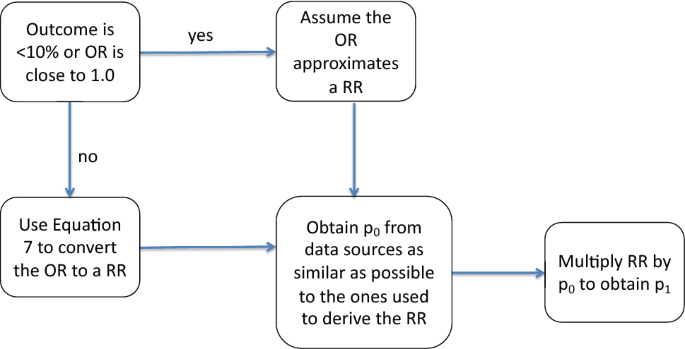



Estimating Transition Probabilities From Published Evidence A Tutorial For Decision Modelers Springerlink
Odds ratio and relative riskWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative riskSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




4 In A Cohort Study The Risk Ratio For Copd For Chegg Com
The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence




Calculating Effect Sizes Pdf Free Download




Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study
This brings us to today's topic Odds Ratio (OR) vs Relative Risk (RR) Odds vs Probability why we love them and why these two cousin statistics continue to confuse us Anyone with a math, science, or medical background has been taught this, and if Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
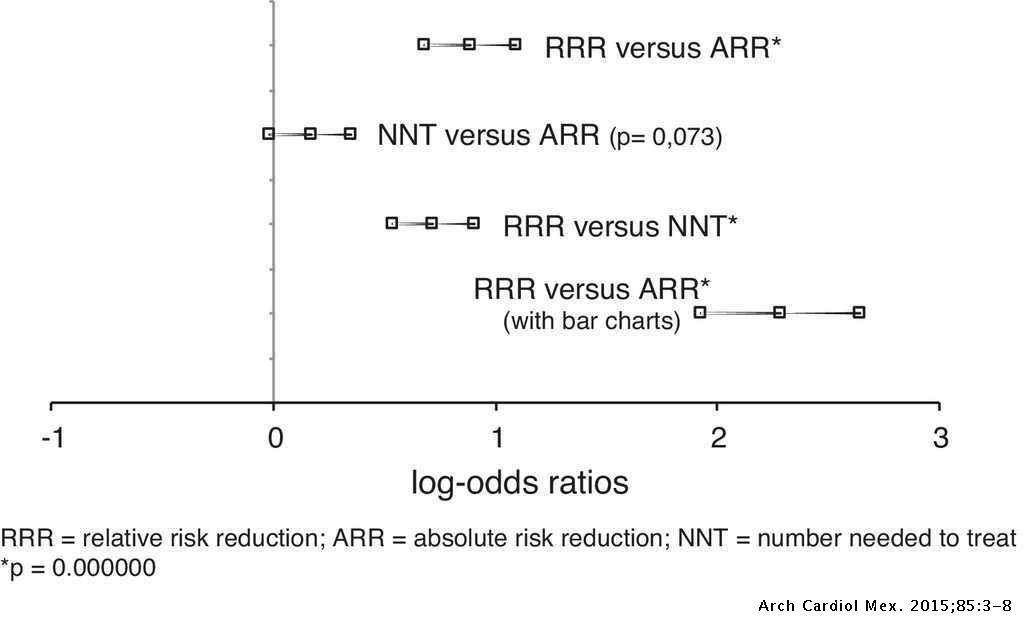
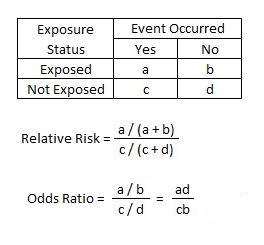
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions We can define the following terms The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



1
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk; The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring In medicine this is often an undesirable health outcome or adverse event




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




The Diagnostic Odds Ratio A Single Indicator Of Test Performance Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measureThe simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variableThe odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio?




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
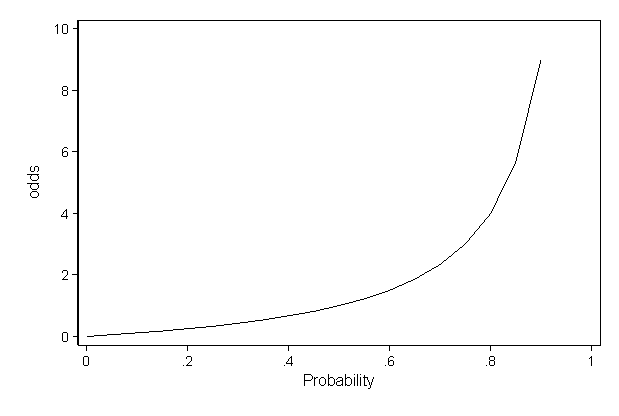



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
Risk Ratio is often expressed as a factor and a whole positive number, such as " is times more likely" The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)




Math3010 Week 6




Odds Ratio Relative Risk
A comparison of odds, the odds ratio, might then make sense OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987) The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programIn health care it is the ratio of the number of people with the event to the number without It is commonly expressed as a ratio of two integers For example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31




Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




Risk Differences And Rate Differences
That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculated




Estimated Relative Risk Rr Compared With Odds Ratio Or For All Download Scientific Diagram




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table



Web Stanford Edu Class Gene210 Files Writeups 12 Odds Ratio And Likelihood Ratio Pdf



Www Journalofdairyscience Org Article S0022 0302 12 1 Pdf



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



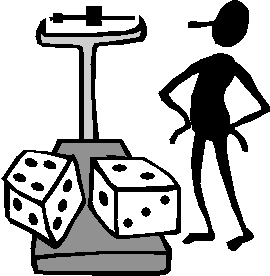
Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico



Healthsci Mcmaster Ca Docs Librariesprovider8 Research Methodology Statistical Notes Relative Risks Versus Odds Ratios Pdf Sfvrsn 2797e56f 4




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
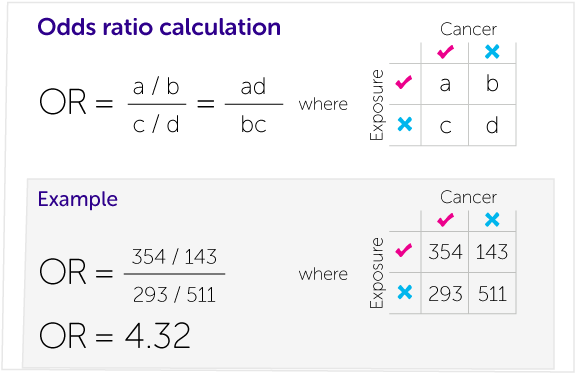



Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
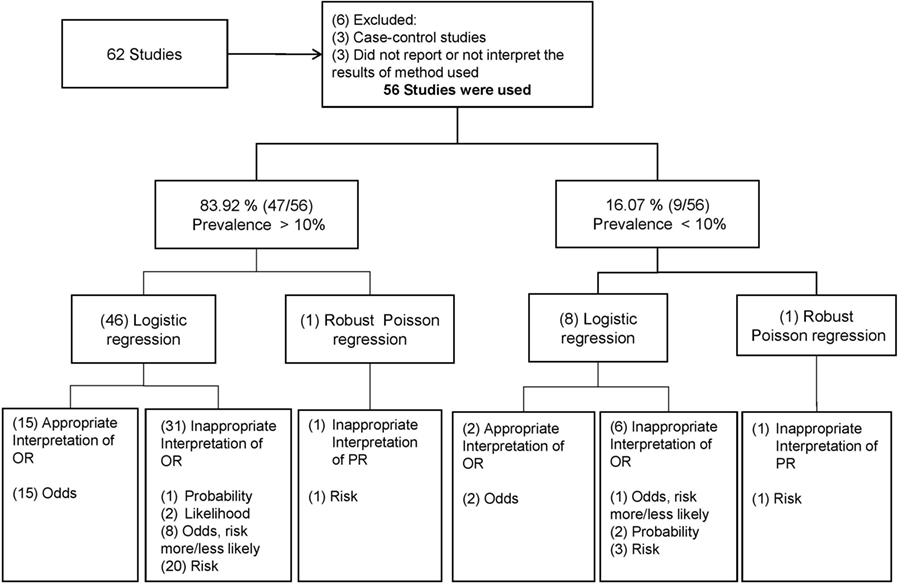



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



1




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons




Odds Ratio Article



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Odds Chegg Com



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
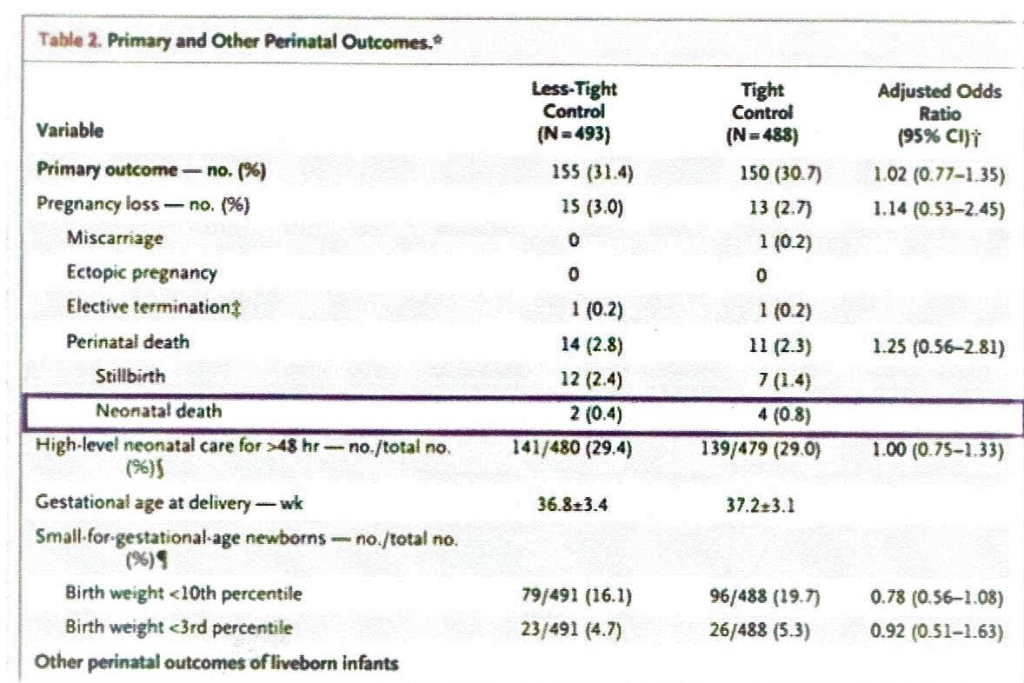



Based On The Data Presented In Table 2 Calculate Chegg Com




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Forest Plot Showing Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio In Al In The Icg Group Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Http Www Math Usu Edu Corcoran Classes Old 04fall51 Notes Lecture04 Pdf




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube



Stats Guidelines For Logistic Regression Models September 27 1999




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Proportions Chi Squared Tests And Odds Ratios




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



1



Relative Risk Article




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout




Comparison Of Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Based On Download Table




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Articles Odds Risks Odds Interpretation Cook 02 Pdf
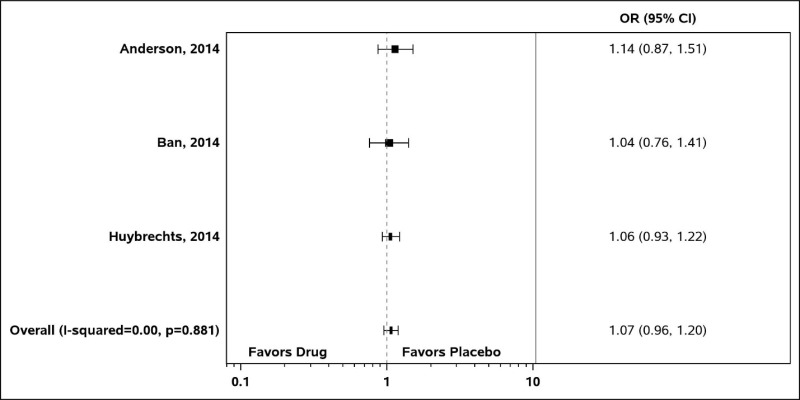



Figure B 2 Pooled Odds Ratios For Cardiac Anomalies For Ssris Versus No Treatment Maternal Fetal And Child Outcomes Of Mental Health Treatments In Women A Systematic Review Of Perinatal Pharmacologic Interventions
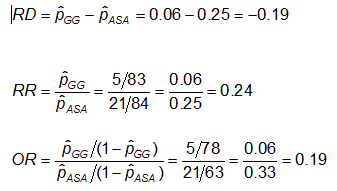



Analysis Of Categorical Data




Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



1




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Power Calculations For Gwass The Smallest Odds Ratio Case Control Download Scientific Diagram




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Case Control Study Wikipedia




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




Pooled Odds Ratio Or Of Risk Of Mortality In Vitamin D Deficient Download Scientific Diagram




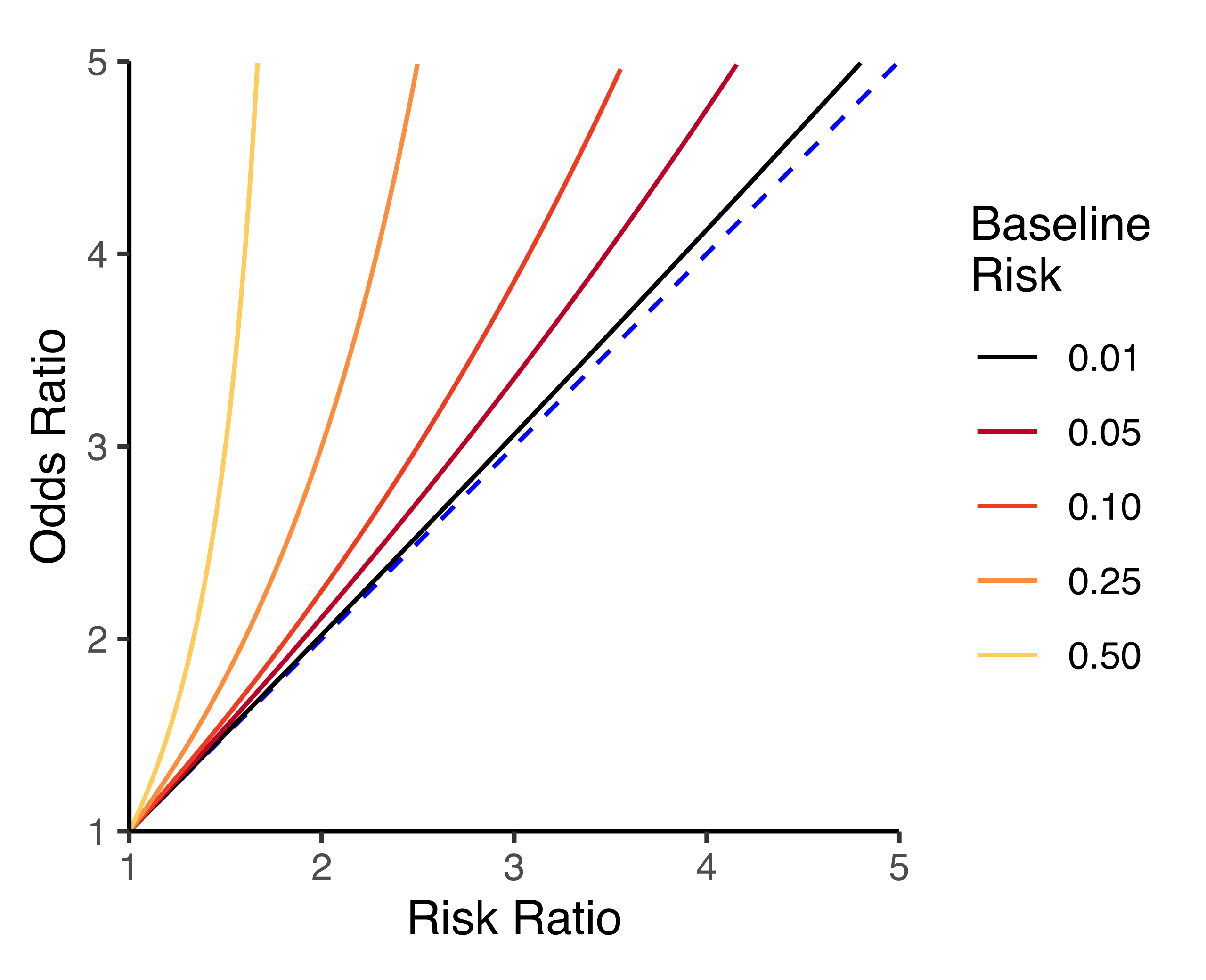
Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿